Unpacking Hydrogen’s Role in Decarbonizing Electricity
Hydrogen’s Role in Decarbonizing the Electricity Sector
Hydrogen constitutes 75% of the elemental mass in our universe.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), it could also play a pivotal role in global decarbonization efforts.
This infographic, created in partnership with the National Public Utilities Council, explores three ways this element could support the decarbonization of the global electricity sector.
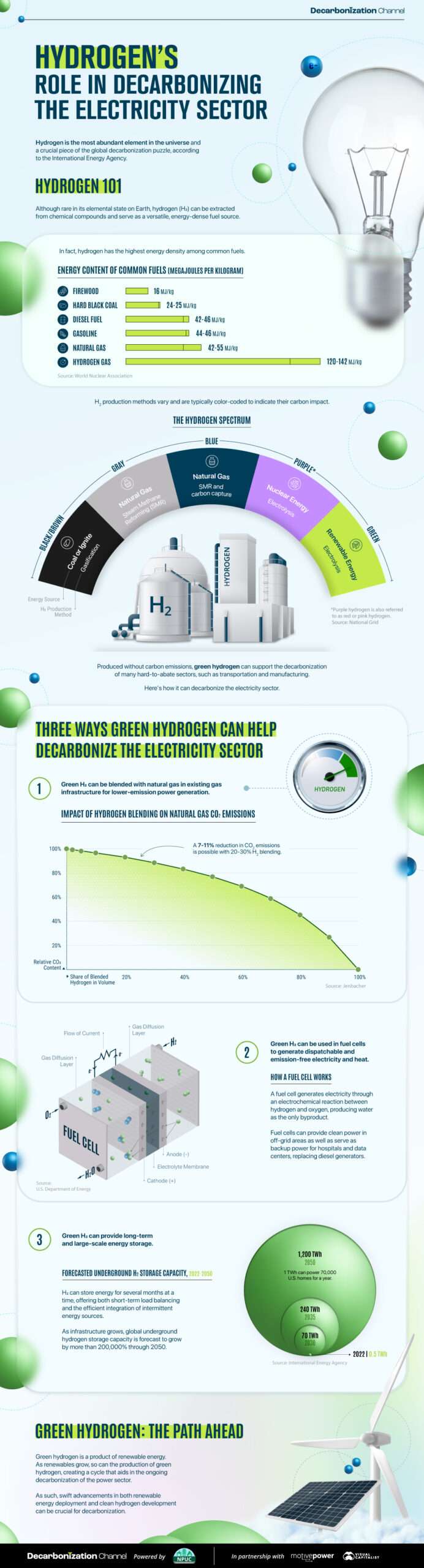
Hydrogen 101
First, let’s get a few basics about hydrogen out of the way.
While abundant in nature, hydrogen is rarely found in its elemental state (H2) on Earth, meaning that it needs to be separated from other chemical compounds, such as water (H2O). Once extracted, however, it becomes a versatile and energy-dense fuel source, containing approximately three times the energy content of gasoline or natural gas.
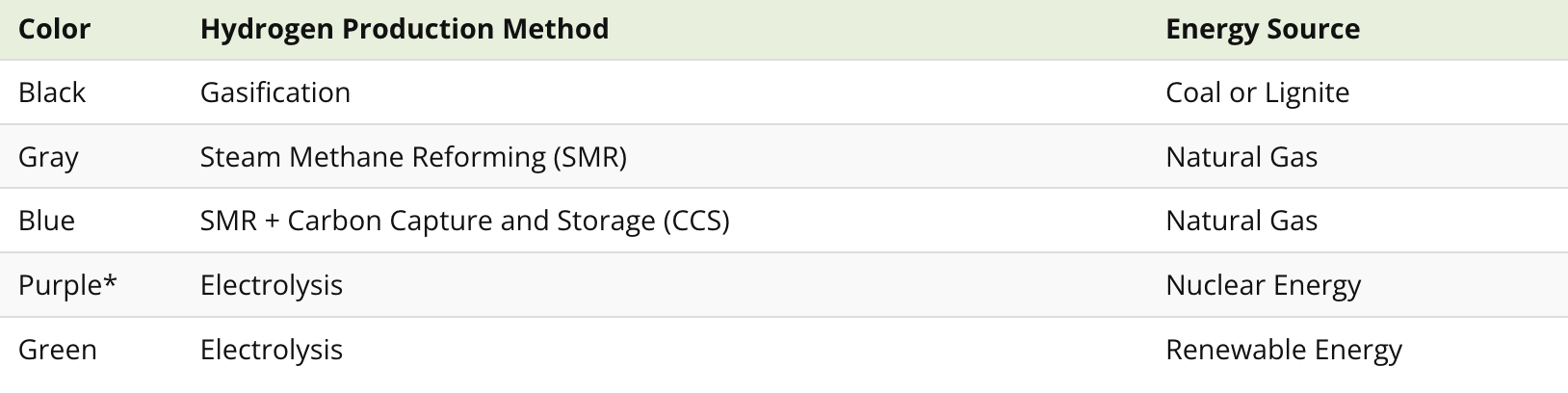
There are several methods to extract hydrogen from compounds. Depending on the production method and energy source, the resulting hydrogen is often categorized by color to show its emission impact.
*Purple hydrogen is also referred to as red or pink hydrogen.
Today, black, gray, and blue hydrogen are used in emission-heavy industries such as petroleum refining and ammonia production.
The technology and infrastructure for purple and green hydrogen, on the other hand, are still taking shape. As they progress, these emission-free sources of hydrogen are expected to play a pivotal role in decarbonizing many hard-to-abate sectors, including power.
Three Ways Green Hydrogen Can Help Decarbonize
Now that we’ve covered hydrogen basics, let’s dive into where emission-free hydrogen can fit in the race to decarbonize our global electricity system.
#1: Hydrogen and Natural Gas Blending
Hydrogen can be blended with natural gas in existing pipeline infrastructure for lower-emission power generation.
According to Jenbacher, a 20–30% hydrogen volume can lead to a 7–11% decrease in CO2 emissions, compared to natural gas on its own.
In 2022, U.S. electricity from natural gas generated 743 million metric tons in the United States. A 9% reduction in emissions through hydrogen blending lowers emissions by 67 million metric tons CO2, all without the need to build new infrastructure.
#2: Fuel Cells
A fuel cell generates electricity through an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, with water as the only byproduct.
By using green or pink hydrogen, fuel cells can provide 100% emission-free electricity that is also efficient, reliable, and dispatchable.
#3: Energy Storage
Energy storage plays a pivotal role in decarbonizing the power sector by balancing the intermittent nature of renewables.
While other technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, can also provide energy storage, hydrogen has a greater potential to offer both large-scale and long-term storage, up to several months at a time.
As technology advances, the IEA predicts that global underground hydrogen capacity will grow by more than 200,000% in the next 30 years, reaching 1,200 TWh in 2050. That amount of energy can power 70,000 U.S. homes for an entire year, underscoring the untapped potential that lies within hydrogen.
Learn more about how electric utilities and the power sector can lead on the path toward decarbonization here.