Ranked: The Cheapest Sources of Electricity in the U.S.
In 2022, the U.S. electricity sector’s reliance on fossil fuels resulted in a staggering 1,539 million tonnes of CO2 emissions.
With the urgent need to decarbonize, however, the question remains: can the transition from fossil fuels to emission-free electricity sources, such as solar, wind, and nuclear power, be accomplished in a financially viable manner?
In this graphic sponsored by the National Public Utilities Council, we seek answers to that question by visualizing the 2023 levelized costs of electricity of various technologies in the U.S., as calculated by Lazard.
Understanding Levelized Cost of Electricity
Levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) is a metric used to assess the cost of generating electricity from a specific power source over its lifetime.
The measure takes into account all of the costs associated with building, operating, and maintaining a power plant, as well as the amount of electricity the plant is expected to produce over its lifetime.
LCOE is a comprehensive way to compare the costs of various electricity generation technologies. It’s also worth mentioning, however, that there is a substantial amount of tax subsidies available for clean electricity generation in the U.S., including the $161 billion in clean electricity tax credits in the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA).
By leveraging these funding opportunities, the LCOE of renewables, nuclear power and energy storage systems has the potential to fall even further, bolstering their competitive edge in the market.
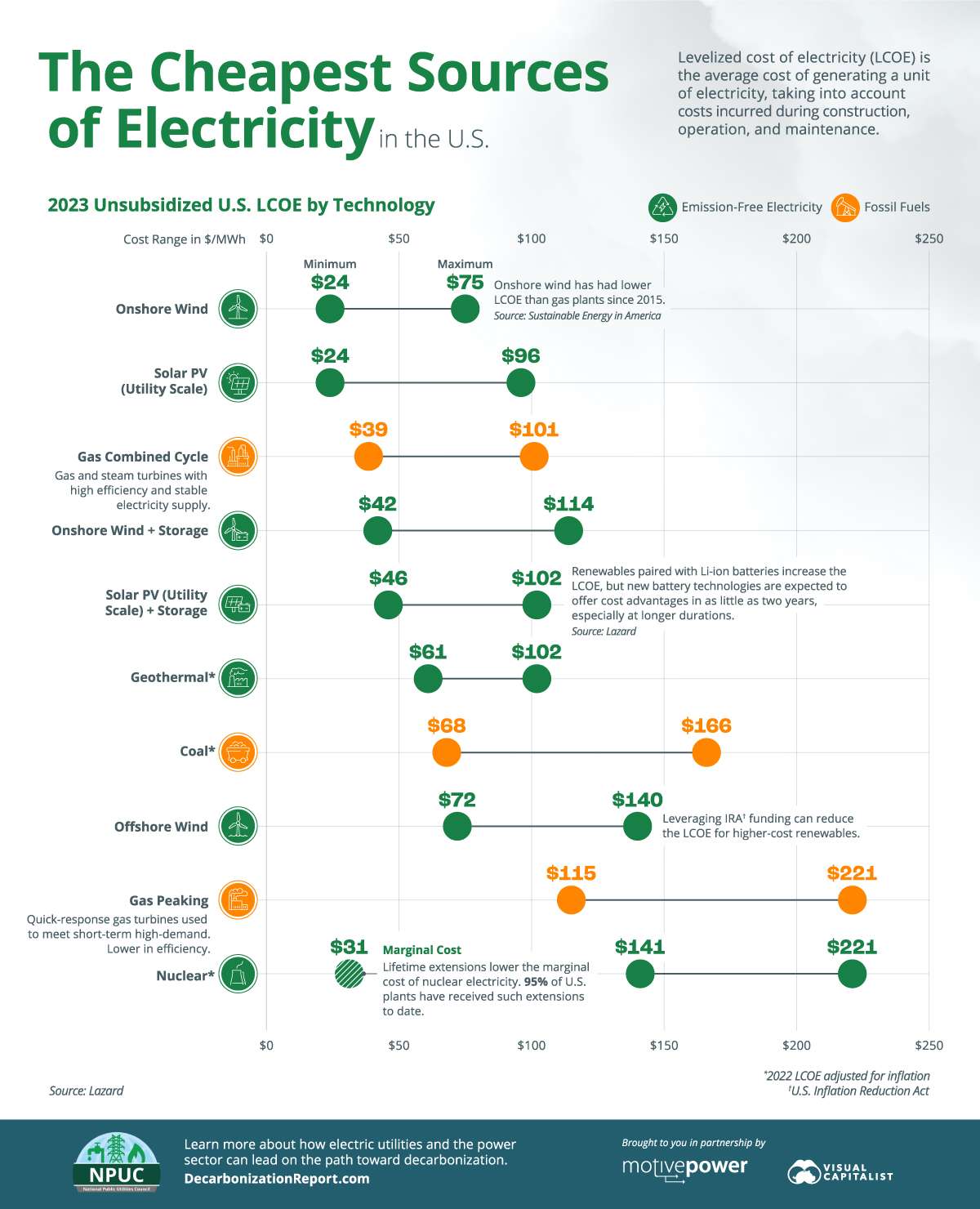
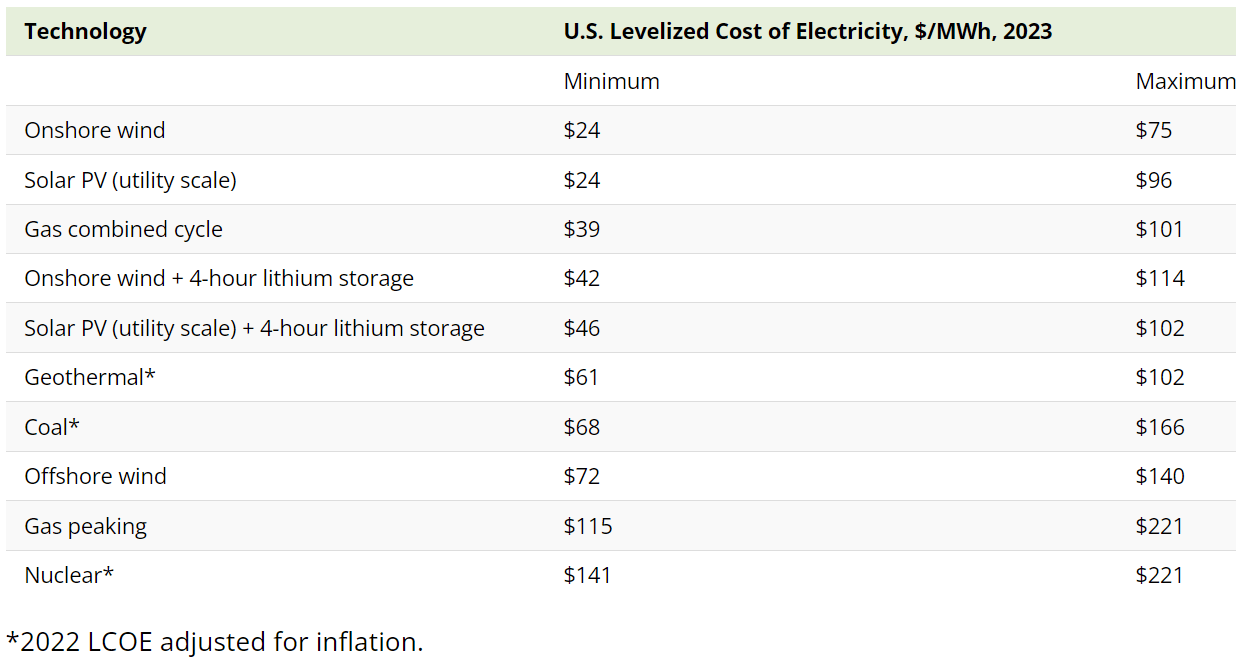
Ranking the Cheapest Sources of Electricity
According to Lazard’s 2023 analysis of unsubsidized LCOE in the U.S., both onshore wind and utility-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) technologies are more cost-effective than combined cycle natural gas power plants.
In the case of onshore wind, this has been true since 2015.
Overall, the data shows us that most emission-free sources are cheaper than fossil fuels. There are, however, some other things to consider:
- Coupling lithium-ion batteries with intermittent energy technologies, such as wind and solar, raises costs by $6-$39/MWh. As new storage technologies, such as electrochemical batteries, mature, however, Lazard expects them to offer cost advantages to lithium-ion ones in as little as two years, especially at longer durations (6+ hours).
- While the LCOE of nuclear seems to be high, license renewals can significantly lower the marginal cost of electricity in these power plants. 88 of the 92 U.S. nuclear reactors have received such renewals in the past.
- The efficiency of generation technologies plays a big role in LCOE. This is especially evident in the high cost of gas peaking power plants.
LCOE Trends for Clean Electricity
There are various factors that can influence the LCOE of clean electricity technologies. These include:
- Financing costs, policy incentives, and government subsidies
- Geographical location, which can influence the availability of renewable resources like sunlight and wind speed
- The availability and cost of key clean energy metals and materials, such as copper, silicon, nickel, zinc and chromium
- The maturity of the technologies, the scale of deployment and the growth in demand
- The overall supply chain, including where most of these technologies are primarily manufactured (China), shipping costs, and disruptions due to global events, such as wars
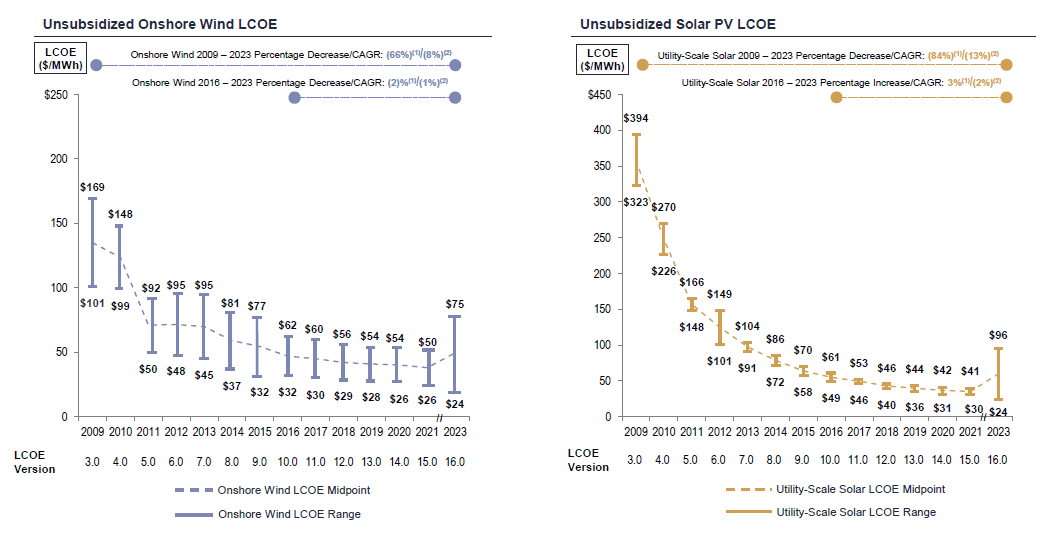
As seen below, the combination of these factors has dramatically pulled down the LCOE of onshore wind and solar PV since 2009, with the exception of 2022-2023.
Source: Lazard
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), however, most of these cost pressures related to inflation and supply chain challenges are easing in 2023, allowing these technologies to remain cost-competitive in today’s volatile fuel-price environment.