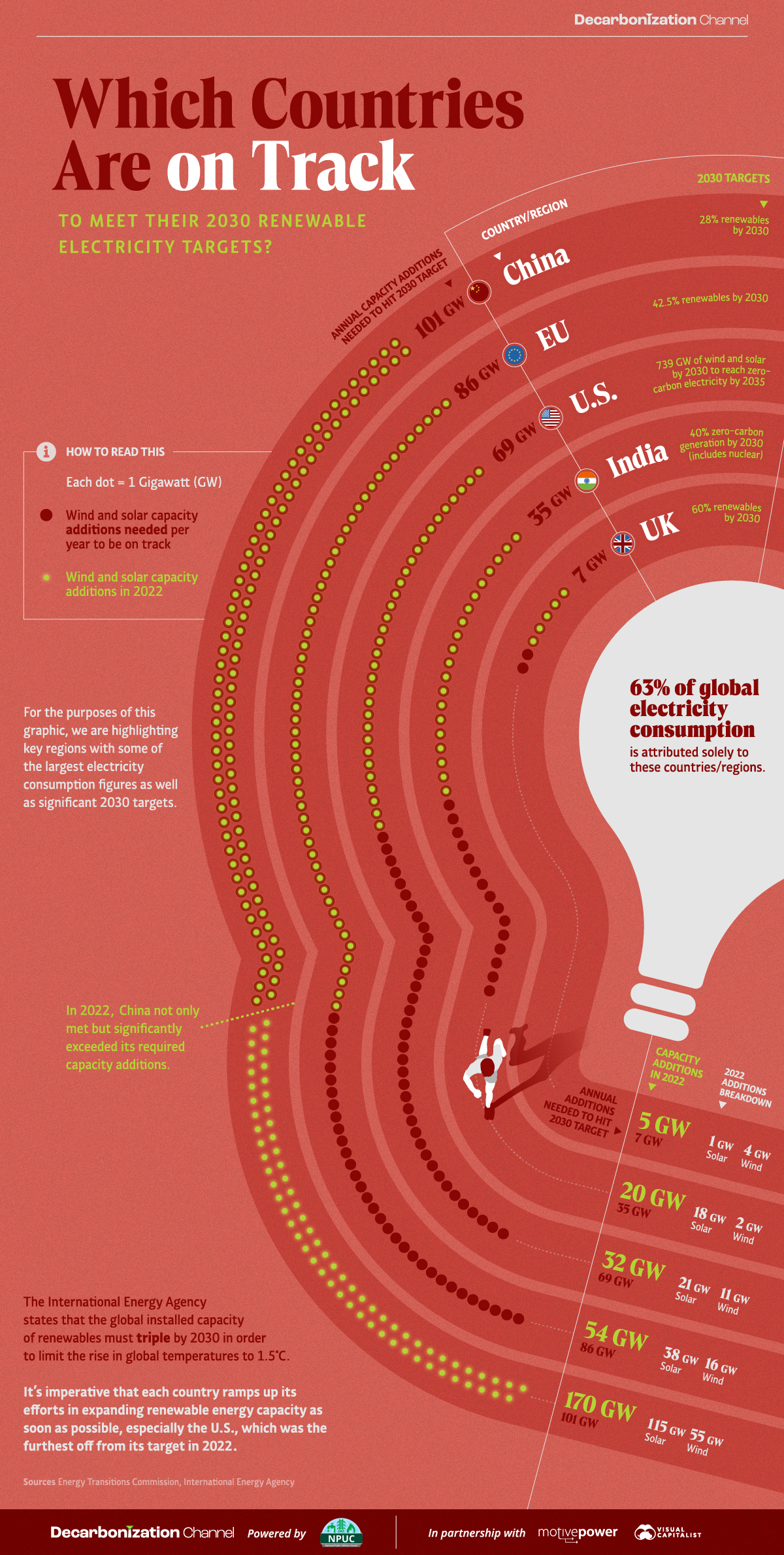
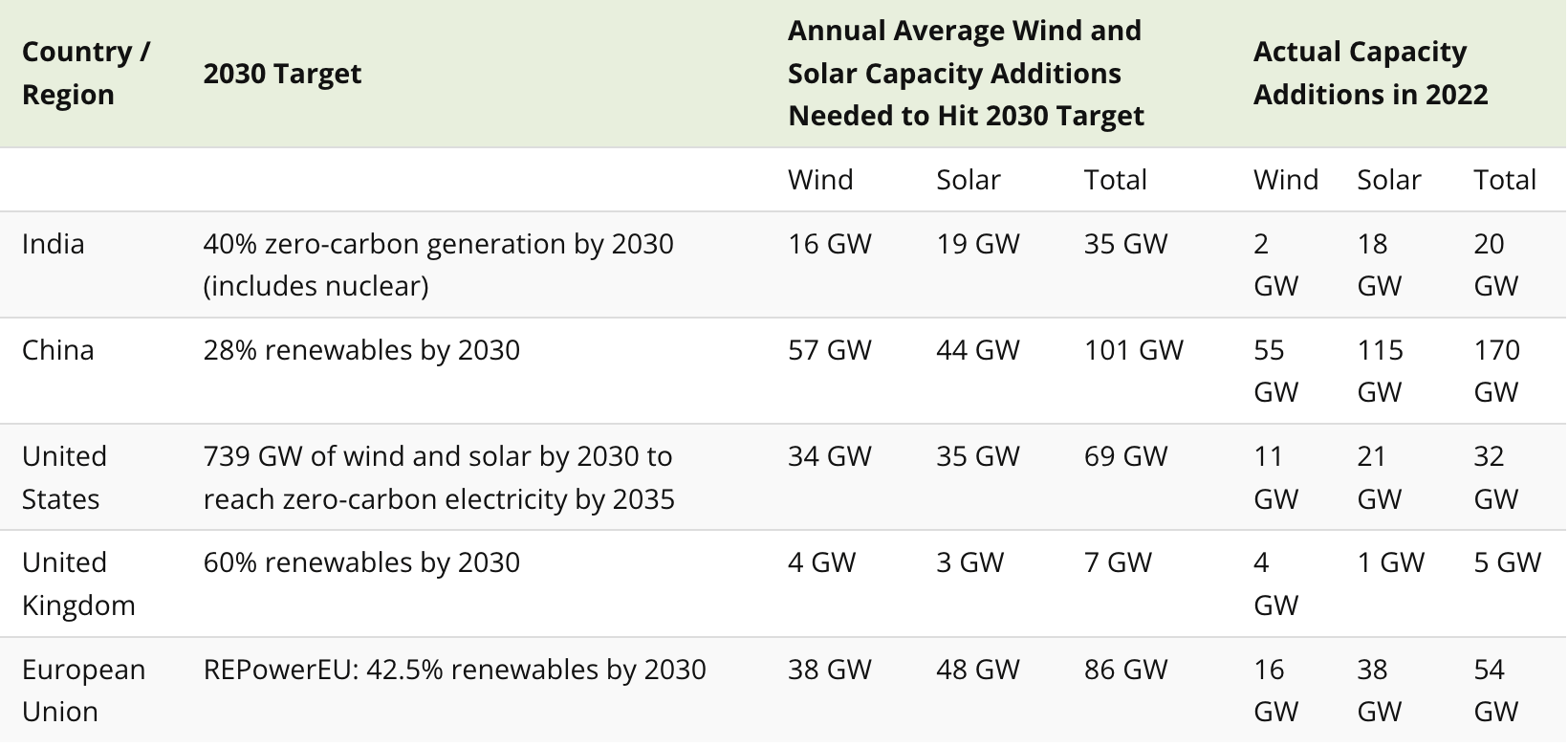
Progress on 2030 Renewable Energy Targets by Country
The International Energy Agency states that the global installed capacity of renewable energy must triple by 2030 to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
This makes the next six years critical in the climate fight, with the upcoming United Nations COP28 event in Dubai representing a great time to assess the progress of countries toward achieving their 2030 targets.
Checking in on Progress
As set out by their Nationally Determined Contributions in the Paris Agreement, many countries, including major electricity consumers such as the U.S., European Union, China, India, and the UK, have set ambitious targets for increasing their solar and wind power generation capacities by 2030.
The data, however, suggests that many are struggling to keep pace with the required annual capacity additions that will allow them to hit these targets.
Currently, China stands out as the only nation on track to meet its 2030 target. In 2022, it not only met but significantly exceeded its required capacity additions to remain on track, adding 168% of the required 101 GW.
Let’s now take a closer look at how each of these countries are faring, comparing how much wind and solar capacity they needed to add with how much they actually did in 2022.
Overall, the U.S. and India were the furthest off from their targets in 2022, adding only 46% and 57% of what was needed, respectively. European countries, on the other hand, made progress but still need substantial annual additions to meet their targets by 2030.
Playing Catch-Up: The Path to 2030
Collectively, the U.S., European Union, China, India, and the UK account for more than 60% of global electricity consumption, underscoring their profound responsibility in decarbonizing their electricity sectors.
Investments in research and development, policy support, and infrastructure development are all crucial pieces of the puzzle when it comes to achieving 2030 targets.
With swift and bold action, these nations have an opportunity to transform the global energy landscape and move the needle toward achieving net-zero on a global scale.
Learn more about how electric utilities and the power sector can lead on the path toward decarbonization here.