Industry Report: Heat Pump Deployment
Heat Pump Adoption Overview
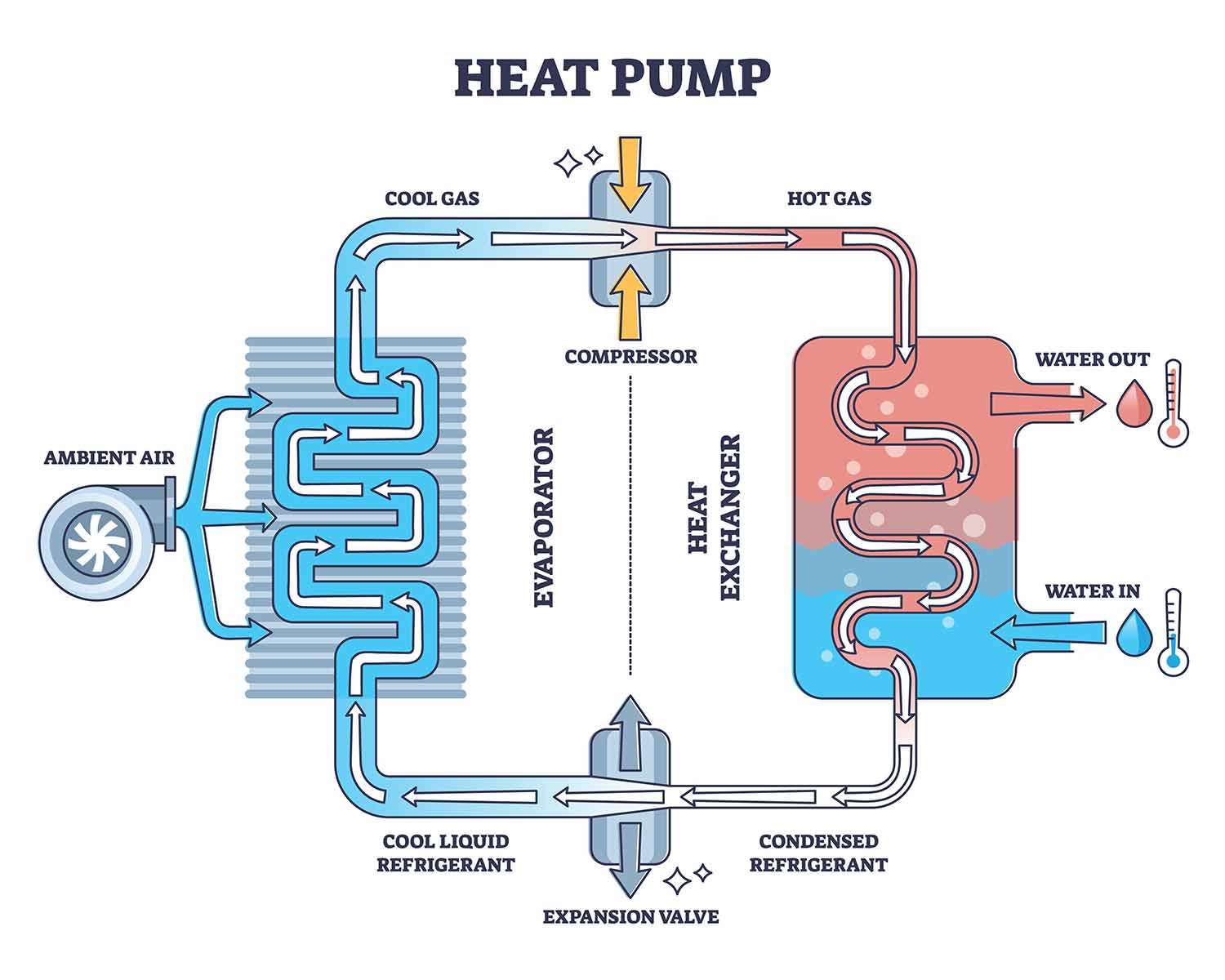
The buildings sector represents over one quarter of global energy-related emissions. Heat pump technologies have consequently emerged as an innovative solution to global decarbonization efforts, offering a cost and energy-efficient method to heat and cool buildings. Heat pumps operate by leveraging minimal amounts of energy to transfer heat from cooler spaces to warmer ones, making it possible to heat and cool buildings and water without excessive emissions. Essentially, heat pumps move heat, rather than generating it through fuel combustion. The potential impact of heat pumps on decarbonization is significant, with the International Energy Agency (IEA) highlighting that potential deployment could reduce global CO2 emissions by over 500 million tons by 2030 – equivalent to the current annual emissions from all cars in Europe. However, heat pumps currently cater to only 10% of global heating needs. To meet the 2050 Net Zero Emissions (NZE) Scenario, the IEA projects that heat pump deployment must triple by 2030. In this vein, the bipartisan U.S. Climate Alliance – a coalition of governors representing over half the United States – recently committed to quadrupling the number of heat pumps deployed between 2020 and 2030. The role of utilities is central in accelerating this transition and meeting legislative mandates for decarbonization. In this context, the National Public Utilities Council (NPUC) has produced industry-leading guidance to support utilities in achieving their climate objectives.
Key Challenges to Adoption
Awareness and Education
One main challenge in the adoption of heat pump technologies is the lack of public knowledge and general awareness. Many consumers and businesses are unfamiliar with the environmental benefits of heat pumps, including their ability to significantly reduce CO2 emissions compared to traditional heating and cooling methods. This gap in understanding extends to economic benefits that heat pumps offer, including proven cost savings over time. As a result, potential users may opt for more familiar but less efficient and more polluting heating and cooling solutions.
Installation Costs
Despite the long-term savings and environmental benefits that heat pumps can offer, the initial installation costs additionally represent a significant barrier to wider adoption. The upfront investment required to install heat pumps in homes with existing fossil-fuel reliant systems may put consumers off. These initial costs not only deter potential buyers but also make it challenging for those with limited financial resources to consider heat pumps as a viable option, despite the eventual energy cost savings and the potential increase in property value.
Retrofitting Challenges
Furthermore, the integration of heat pump systems into older buildings presents significant technical and structural challenges. Antiquated building structures were not designed with the installation of modern heating and cooling systems in mind, making the retrofitting process complex and potentially costly. These challenges can include inadequate space for equipment, the need for significant ductwork modifications, or even structural reinforcements to accommodate the new system. In some cases, very old buildings may not be suitable for heat pump systems at all.
Technical Expertise
Finally, the successful deployment and maintenance of heat pump systems relies on the availability of skilled technicians and installers specialized in this technology. Currently, there is a notable shortage of such professionals in the industry, which contributes to a general gap in knowledge and a hindrance to deployment. Specialists are likely to recommend systems they’re more comfortable with, rather than systems that may be more environmentally and economically beneficial to consumers. Continuous training and upskilling of the workforce is needed. The lack of qualified professionals not only impedes the installation process but also affects consumer confidence in the technology, as potential users may be concerned about the availability of support and the quality of installation services.
Best Practices for Accelerating Deployment
Midstream vs. Downstream Incentives
In various applications across the United States and throughout Europe, the effectiveness of “midstream” vs “downstream” incentives has proven significant. Midstream incentives are directed at contractors and installers, incentivizing them to recommend and install heat pumps, while downstream incentives target the end-users or consumers, offering rebates or financial aid upon purchase or installation. Experience has shown that midstream incentives directed at contractors are far more effective in accelerating deployment. By engaging contractors directly, these incentives encourage the professionals who are most knowledgeable and influential in the consumer decision-making process to prioritize and recommend heat pumps. Incentivizing contractors to install heat pumps through rebates, tax credits, or other funding programs incentives effectively positions them as the key sales agents in the process.
Digital Platforms
In various service territories where heat pump programs are offered, navigating key information regarding installations, costs, and funding support can be difficult and complex. Developing comprehensive digital platforms that serve as “one-stop-shops” for heat pump installation significantly simplifies the process for consumers and contractors alike. Such platforms consolidate all necessary information, from the benefits and technical specifications of heat pumps to details about available financial incentives and a directory of qualified installers. By providing a centralized source of information, these platforms can demystify the process of selecting, financing, and installing heat pump systems. They facilitate easier decision-making for consumers and streamline the administrative aspects of incentive programs for contractors, contributing to a smoother, more efficient transition to energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions.
Educational and Marketing Initiatives
Educational and marketing initiatives play a pivotal role in increasing public awareness and understanding of heat pumps. These campaigns are essential for highlighting the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits of heat pumps compared to traditional heating and cooling methods. By utilizing a mix of traditional media, social media, workshops, and community events, these initiatives can effectively reach a wider audience, informing and showcasing the tangible benefits of heat pump technology.
Workforce Development
The gap in technical expertise among contractors and installers regarding heat pump technology is a significant barrier to its widespread adoption. Workforce development initiatives aimed at engaging with and training these professionals are crucial. By providing access to specialized training programs, certifications, and continuous learning opportunities, these initiatives can equip the workforce with the necessary skills and knowledge to install and maintain heat pump systems efficiently. This not only improves the quality of installations but also boosts consumer confidence in the technology, as they can rely on a network of knowledgeable professionals for their heat pump needs.
Low-Income Support Programs
Ensuring equitable access to heat pump technology is essential, especially for low-income communities that stand to benefit the most from reduced energy costs and environmental impact. Leveraging federal and state initiatives to support these communities through targeted financial incentives, grants, and educational programs can make a significant difference. These support programs can help overcome the initial cost barriers and ensure that the benefits of heat pump technology are accessible to all, regardless of economic status. By prioritizing inclusivity and support for disadvantaged communities, such programs not only advance environmental and energy efficiency goals but also contribute to social equity and the reduction of energy poverty.
For More Information
For a deeper understanding of the National Public Utilities Council’s (NPUC) research, and to explore how we can assist you in adopting these industry-leading strategies, we invite you to reach out to us. Our team is ready to provide you with tailored insights and support, ensuring you are well-equipped to advance your decarbonization goals. Don’t hesitate to contact us to discuss how we can work towards a more sustainable future.
Learn more about how electric utilities and the power sector can lead on the path toward decarbonization here.