Breaking Down Clean Energy Funds in the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), signed into law on August 16, 2022, is the largest climate legislation in U.S. history.
Along with fighting inflation and boosting domestic manufacturing, the IRA ultimately aims to help the U.S. achieve its goal of reaching net-zero emissions by 2050.
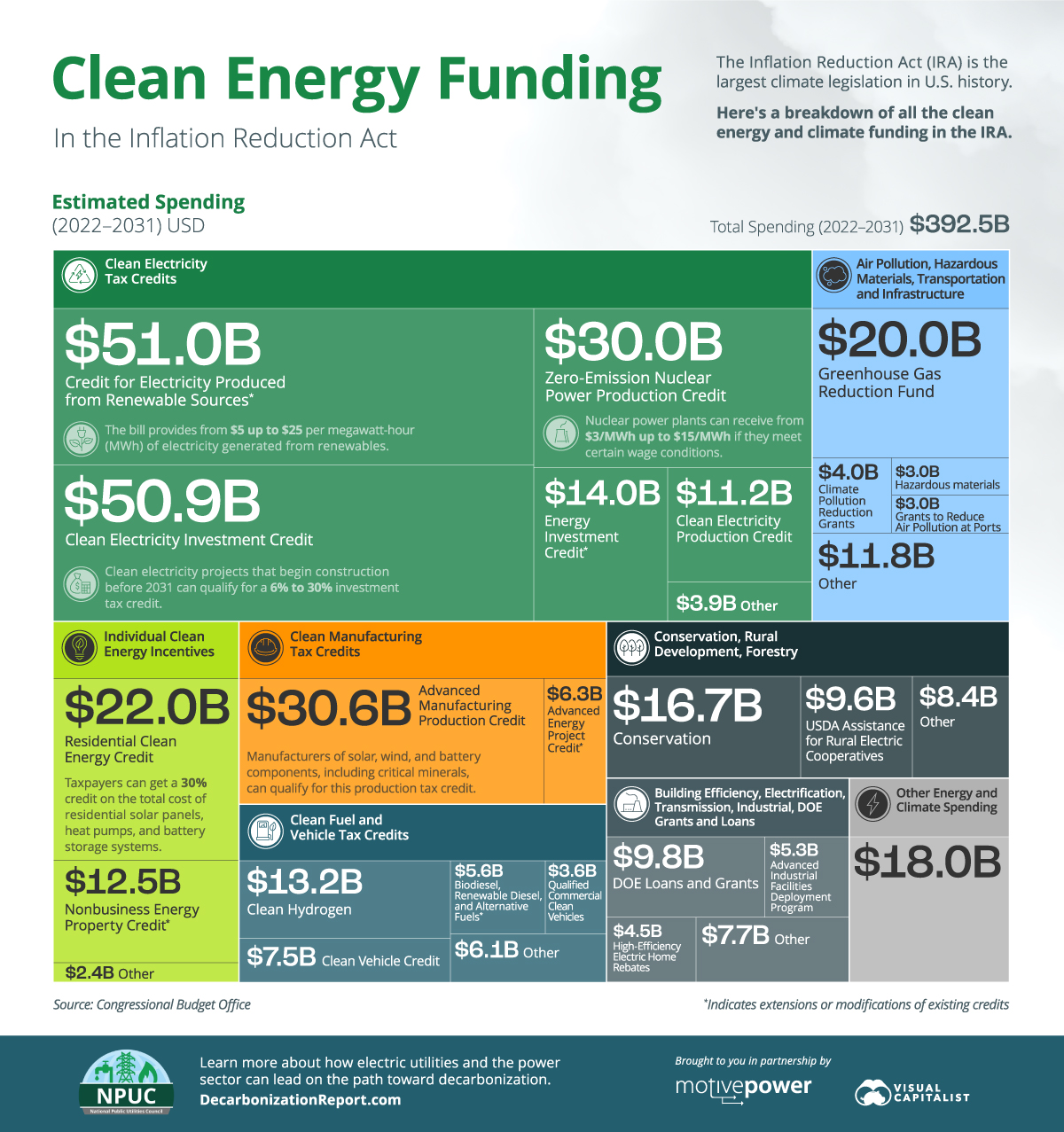
This infographic, sponsored by the National Public Utilities Council, breaks down the $392.5 billion in clean energy and climate spending in the Inflation Reduction Act, based on estimates from the Congressional Budget Office.
Note: The figures in the graphic and article refer to the IRA’s estimated spending for each program. Spending estimates tend to be lower than the total amount of funds allocated by the act.
Deconstructing the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022
The IRA’s clean energy and climate spending can be broken down into seven broader categories:
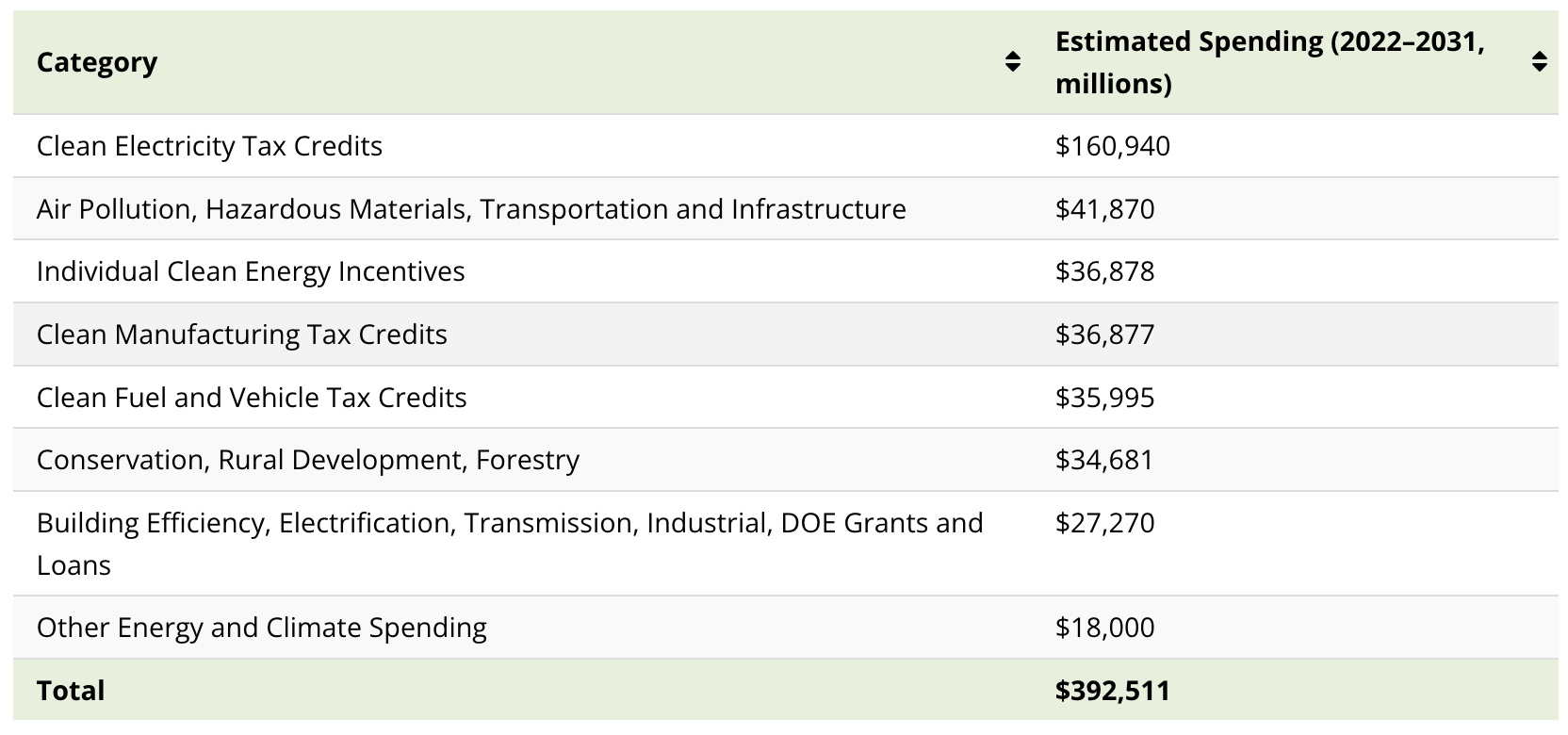
Clean Electricity Tax Credits, which include the Clean Electricity Production Tax Credit (PTC) and Investment Tax Credit (ITC), account for the largest share of climate spending at 41% of the $392.5 billion.
Furthermore, the IRA mobilizes around $42 billion for programs aimed at air pollution, hazardous materials, and infrastructure. The Individual Clean Energy Incentives and Clean Manufacturing Tax Credits programs each receive $37 billion to incentivize residential clean energy use and domestic manufacturing of clean technology components.
Below, we’ll unpack the IRA’s clean energy spending in further detail.
Clean Electricity Tax Credits
Of the $161 billion of funding for Clean Electricity Tax Credits, $132 billion is for just three programs.
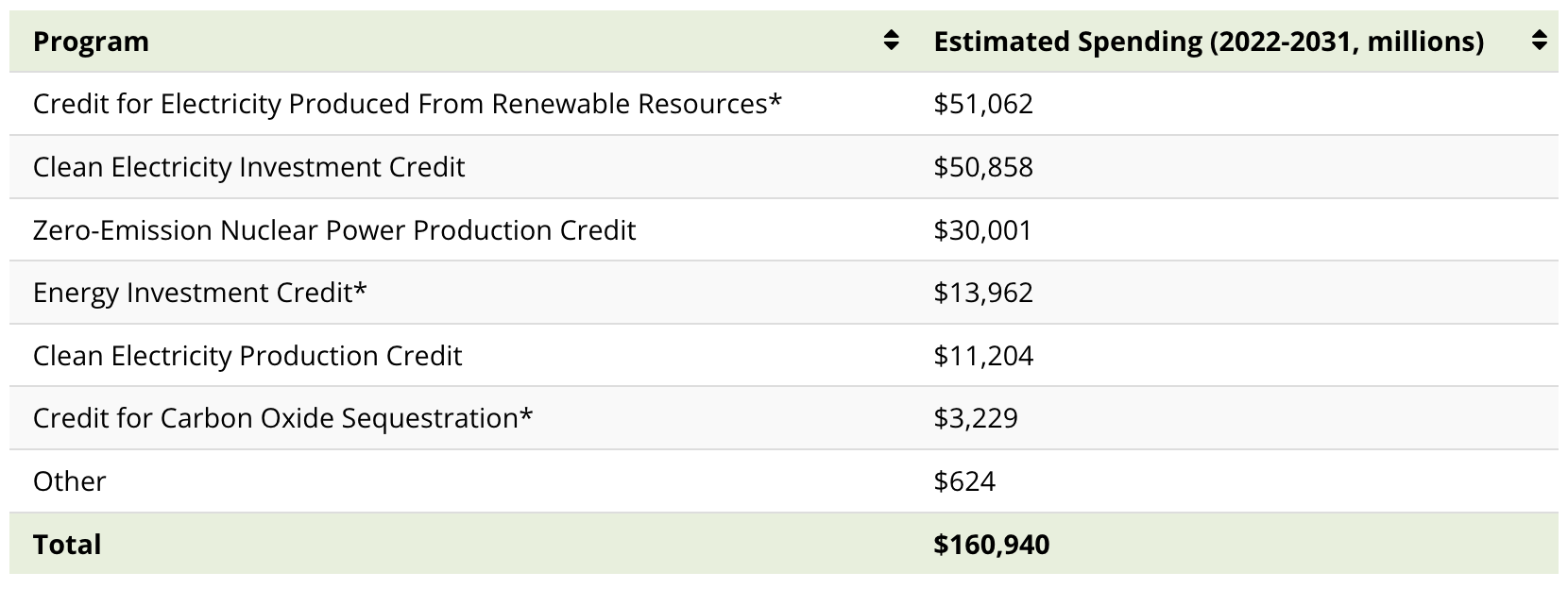
*Indicates extensions or modifications of existing credits.
The Credit for Electricity Produced from Renewable Sources is a PTC that provides from $5 to $25 per megawatt-hour (MWh) of electricity generated from renewable facilities. Wind, solar, geothermal, marine, biomass, hydro, and landfill gas facilities are eligible for this credit.
The Clean Electricity Investment Credit is an ITC with a base credit of 6% (rising to 30% if other requirements are met) on the total cost of installed equipment for a zero-emissions power generation facility. Besides renewables, nuclear, fuel cells, and battery storage systems qualify for this credit.
Nuclear is set to get a $30 billion boost through the Zero-Emission Nuclear Power Production Credit, which offers from $3 up to $15 per MWh of electricity generated from nuclear reactors. This is applicable for all reactors in service in 2024 and continues through 2032.
Clean electricity projects can either claim the PTC or the ITC (not both). Projects with high capital costs are likely to benefit from the ITC. On the other hand, projects with high capacity factors could benefit from credits per unit of electricity from the PTC.
Air Pollution, Hazardous Materials, Transportation and Infrastructure
Nearly half the spending for programs in this category–around $20 billion—is for the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Reduction Fund.
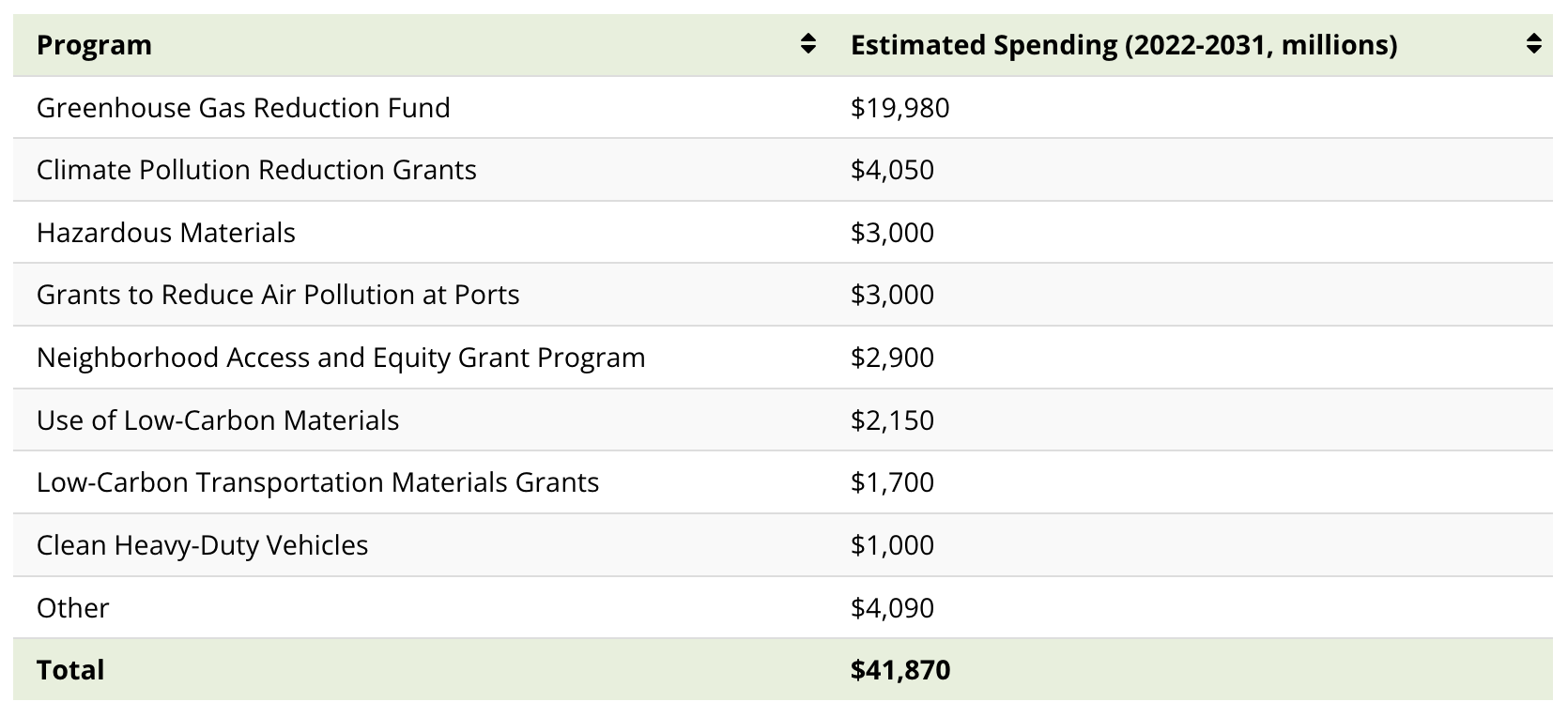
The GHG Reduction Fund, managed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), aims to provide grants for clean energy and climate projects that reduce GHG emissions, with a focus on low-income and disadvantaged communities.
Similarly, other policies in this category provide the EPA with funding for grants to reduce various kinds of air pollution and curb hazardous material usage.
Individual Clean Energy Incentives
The IRA provides various tax credits to incentivize clean energy use and energy efficiency in American households.
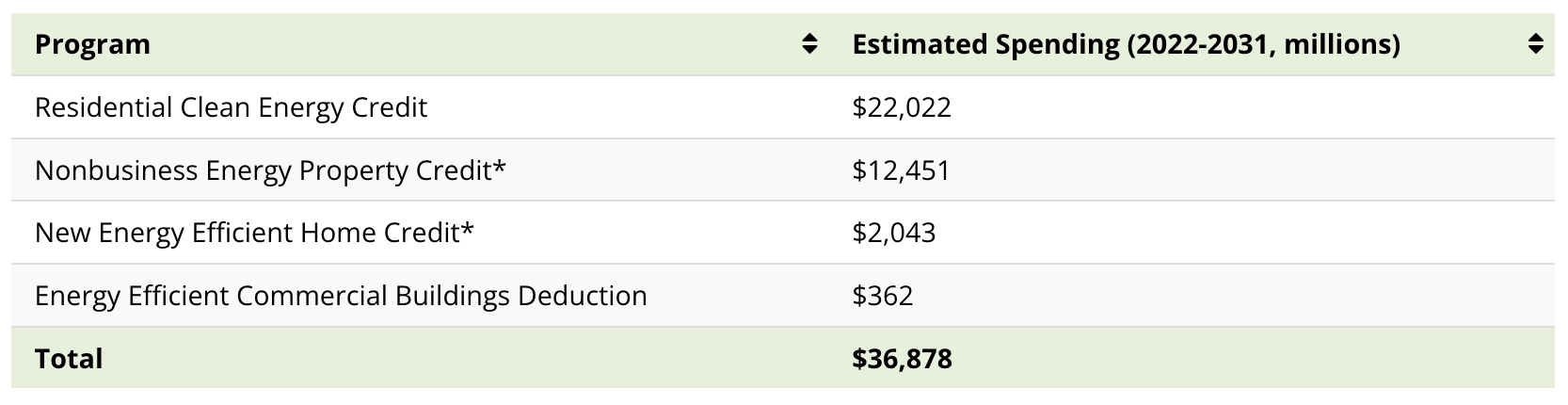
*Indicates extensions or modifications of existing credits.
The Residential Clean Energy Credit, accounting for $22 billion in spending, provides a 30% credit on the cost of residential clean energy equipment. This includes rooftop solar panels, geothermal heating systems, small wind turbines, and battery storage systems.
The Nonbusiness Energy Property Credit, now known as the Energy Efficient Home Improvement Credit, offers up to $3,200 annually for energy-efficient home upgrades, including insulation, heat pumps, efficient doors, and more.
Clean Manufacturing Tax Credits
Besides energy generation, the IRA incentivizes domestic manufacturing of clean technologies with the following credits:
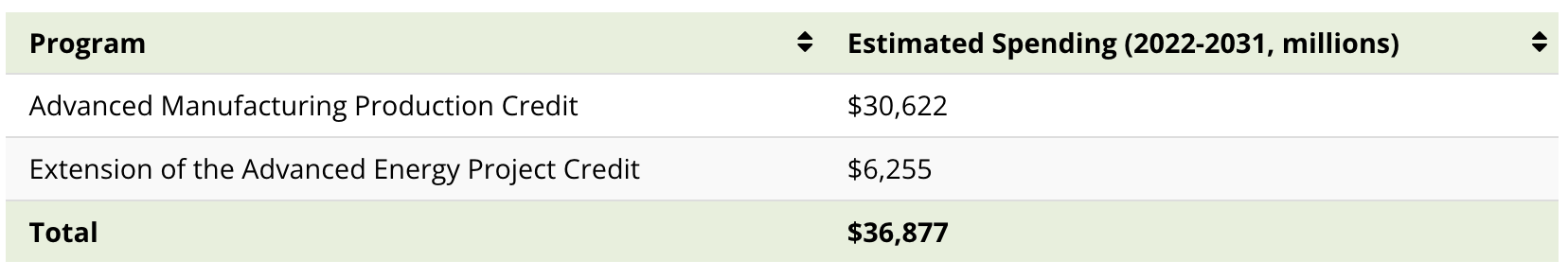
The Advanced Manufacturing Production Credit is a tax credit for the domestic production of solar and wind energy components, inverters, battery components, and critical minerals. The credit for critical minerals is permanent, unlike credits for other items, which will phase out in 2032.
Other Climate Funding in the IRA
In addition to the policies above, the IRA sanctions another $116 billion for clean energy and climate programs.
This includes incentives for clean hydrogen production, electric vehicle purchases, and alternative fuels. Furthermore, the Department of Energy receives around $9.8 billion for clean energy innovation and infrastructure loan and grant programs.
The act also invests in environmental conservation and rural development. It includes an estimated $9.6 billion in assistance for rural electric cooperatives, along with other incentives for energy efficiency and renewable energy.
With billions in climate funding, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 is set to provide a significant boost to America’s clean energy plans. According to an assessment by the Department of Energy, the IRA could help reduce economy-wide GHG emissions to 40% below 2005 levels by 2030, marking a major milestone on the road to net-zero.